Ethereum system, which is the most prominent commercial network in the field of encryption and deals with transactions worth billions of dollars, is becoming increasingly centralized. This raises questions about the security, stability, and innovation of the network, as well as its alignment with the original vision of decentralization.
What is Ethereum’s Centralization?
Ethereum centralization refers to the concentration of power and influence over the network in the hands of a few entities or individuals. This can happen in various aspects of the network, such as:
Validation:
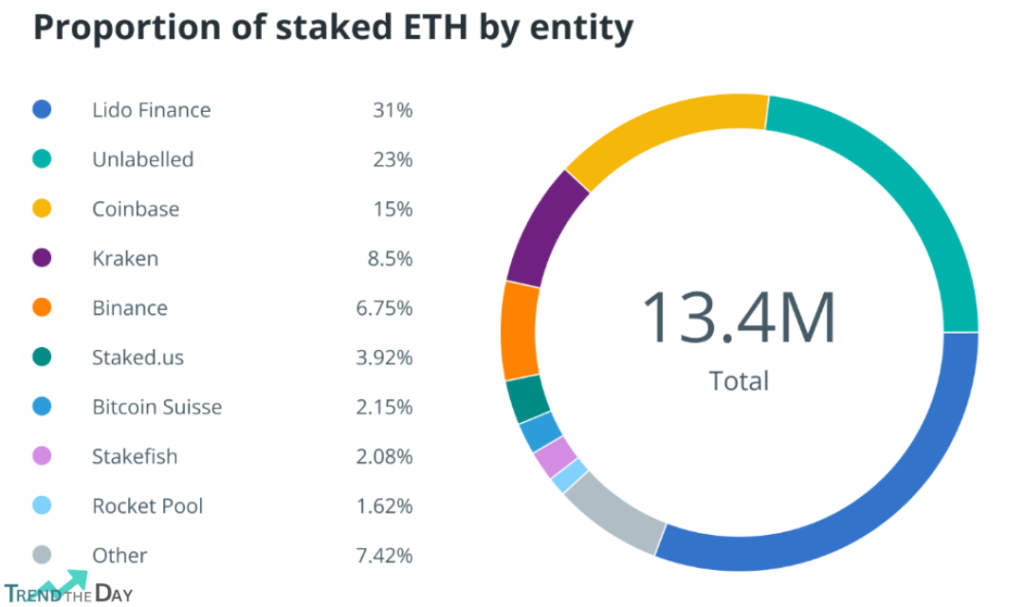
The process of ordering and verifying transactions on the blockchain. Ethereum’s Centralization recently switched from a proof-of-work (PoW) system, where miners use computational power to secure the network, to a proof-of-stake (PoS) system, where validators stake Ether tokens to participate in consensus. PoS is supposed to be more energy-efficient, scalable, and democratic than PoW, but it also introduces new risks of Ethereum’s centralization. For example, validators with more stake have more voting power and rewards, which can create a positive feedback loop that favors the rich and discourages new entrants. Validators can also collude or be compromised by malicious actors, which can lead to network attacks or censorship.
Relaying:
The process of batching and broadcasting transactions on the network to ensure efficient and timely processing. Relayers are third-party services that act as intermediaries between users and validators. They can help users optimize their transaction fees and execution speed, as well as extract value from miner extractable value (MEV), which is the difference between the optimal and actual ordering of transactions. However, relayers can also introduce centralization risks, such as reducing the diversity and redundancy of transaction sources, creating information asymmetry and market inefficiencies, and enabling front-running and other forms of MEV exploitation.
Development:
The process of creating and maintaining the code and protocols that run the network. Ethereum has a large and active community of developers who contribute to its innovation and improvement. However, some developers have more influence and authority than others, such as those who work for the Ethereum Foundation, which supports the network, or those who lead influential projects or organizations within the ecosystem. Developers can also face external pressures or incentives from regulators, investors, users, or competitors, which can affect their decisions and priorities.
Usage:
The process of interacting with and benefiting from the network. Ethereum has a diverse and growing user base that includes individuals, businesses, institutions, and governments. However, some users have more access and advantages than others, such as those who have more resources, knowledge, or connections. Users can also face barriers or challenges that limit their participation or satisfaction, such as high fees, low scalability, poor usability, or regulatory uncertainty.
Why is Ethereum’s Centralization a Problem?

Ethereum centralization can have negative impacts on the network and its stakeholders, such as:
Security:
Centralization heightens the network’s vulnerability to attacks or disruptions by malicious actors who can exploit weaknesses or dependencies within centralized entities. Validators, relayers, or developers with significant influence can become attractive targets for attackers.
Stability: Centralization increases the network’s susceptibility to failures or errors, stemming from honest actors making mistakes or engaging in disagreements. Malfunctions in validators, relayers, or developer errors can have unintended consequences, affecting network performance and compatibility.
Innovation:
Centralization impedes openness to changes or innovations introduced by more forward-thinking participants. Validators, relayers, or developers may resist protocol upgrades or proposals that challenge their profits or influence.
Decentralization: The very essence of Ethereum’s original vision, grounded in principles of openness, inclusiveness, fairness, and democracy, can be compromised by centralization. Oligopolies or monopolies may emerge among validators or relayers, while developers could establish hierarchies dictating the network’s direction and culture.
More to know : Opposing Centralization in Ethereum Staking
https://www.msn.com/en-us/money/markets/opposing-centralization-in-ethereum-staking/ar-AA1hrOlq
How Can Ethereum Centralization Be Addressed?
Ethereum centralization is not a new or unique problem. It has been recognized and discussed by various stakeholders in the network for a long time. There are also various solutions and strategies that have been proposed or implemented to address it, such as:
Education:
Raising awareness and understanding among all stakeholders about the causes and consequences of centralization. This empowers informed decision-making that supports decentralization.
Incentives:
Aligning the incentives, rewards, and penalties for all stakeholders with the goal of decentralization. This encourages individuals to pursue their self-interests while also contributing to the common good.
Regulation:
Establishing and enforcing rules and standards that promote and protect decentralization within the network. This helps prevent and resolve disputes or abuses that could undermine decentralization.
Innovation:
Developing and adopting novel technologies and protocols that enhance decentralization within the network. This enables the network to overcome the limitations and challenges that hinder its path toward greater decentralization.
Conclusion
Ethereum’s centralization challenge is a complex, evolving issue that necessitates ongoing vigilance and evaluation. It is a collective challenge that requires cooperation and participation from all stakeholders in the Ethereum community. Through collaborative efforts, the Ethereum network can maintain its security, stability, innovation, and commitment to decentralization.
If you want to know more about Cryptocurrencies :
https://trendtheday.com/india-has-taken-to-regulate-cryptocurrencies/
